Windows 11 Introduces Direct Process Termination from Taskbar

Microsoft's latest operating system, Windows 11, will soon offer a new feature allowing users to directly stop a process from the taskbar. This marks a departure from previous versions of Windows, where users could only do so through Task Manager.
The new feature will be included in Build 25300 and higher versions of Windows 11. Although the function is not yet operational, it has been spotted by users in those builds when they right-click on an open task in the taskbar. They can now close a window and terminate a process directly, making it more intuitive and easier to use.
Before this update, users had to close a task via Task Manager, which has been the only way to terminate a process for many years. While the new feature is not yet available to everyone, users of the tool ViVe can manually enable it with the command "vivetool /enable /id:42592269." However, the functionality is still lacking.
The ability to end a process directly from the taskbar is a welcome addition to Windows 11's user interface. This feature could save time for users who frequently manage multiple tasks and processes on their computers. With this feature, users will no longer have to go through Task Manager to terminate a process, making it easier to quickly close a non-responsive program or application, without having to switch between multiple windows or navigate through various menus.
As with any new update, it may take some time for the feature to become available to everyone. Nevertheless, Microsoft's continued efforts to improve the Windows operating system suggest that users can expect more useful and user-friendly features in the future. It is a small but important change that will likely be welcomed by many Windows 11 users.
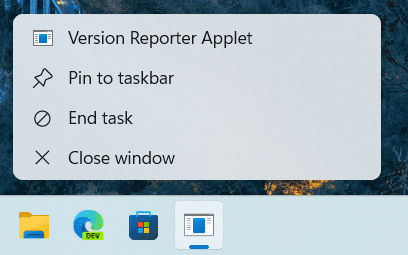
What are current other options to end a task?
In addition to the new option of terminating a process directly from the taskbar in Windows 11, there are other ways to force end a task without using the GUI or Task Manager.
One option is to use the Command Prompt. Users can use the "taskkill" command with the "/F" flag to force terminate a process. They can specify the executable name using the "/IM" flag or the process ID using the "/PID" flag. For example, "taskkill /F /IM notepad.exe" will forcefully terminate the Notepad process.
Another option is to use PowerShell. Users can utilize the "Stop-Process" cmdlet with the "-Name" parameter to specify the executable name or the "-ID" parameter to specify the process ID. They can also use the "-Force" parameter to forcefully terminate the process. For example, "Stop-Process -Name notepad -Force" will forcefully terminate the Notepad process.
These methods can be useful for advanced users or for situations where the GUI or Task Manager is not available or practical to use.
Another practical way to force terminate a task in Windows is to use the keyboard shortcut "Alt + F4". This shortcut can be used to close an active window or application, and it can also be used to force terminate a non-responsive application.
While this method can be useful for quickly terminating a non-responsive application, it may not be as effective as using the Task Manager or Command Prompt for terminating a process. Additionally, using this method may cause the application to lose any unsaved data, so it should be used with caution.

